
Every day, NASA’s satellites orbit Earth, capturing a wealth of information that helps us understand our planet. From monitoring wildfires to tracking climate change, this vast trove of Earth Science data has the potential to drive scientific discoveries, inform policy decisions and support industries like agriculture, urban planning and disaster response.
But navigating the over 100 petabytes of collected data can be challenging, which is why NASA has collaborated with Microsoft to explore the use of a custom copilot using Azure OpenAI Service to develop NASA’s Earth Copilot, which could transform how people interact with Earth’s data.
Geospatial data is complex, and often requires some level of technical expertise to navigate it. As a result, this data tends to be accessible only to a limited number of researchers and scientists. As NASA collects more data from new satellites, these complexities only grow and may further limit the potential pool of people able to draw insights and develop applications that could benefit society.
Recognizing this challenge, NASA embarked on a mission to make its data more accessible and user-friendly. As part of its Transform to Open Science initiative, the agency seeks to democratize data access, breaking down technical barriers to empower a diverse range of audiences, from scientists and educators to policymakers and the general public.
The challenge: Navigating the complexity of data
NASA’s Earth Science Data Systems Program is responsible for collecting an incredible variety of data from spaceborne sensors and instruments. This data spans everything from atmospheric conditions to land cover changes, ocean temperatures and more. However, the sheer scale and complexity of this information can be overwhelming. For many, finding and extracting insights requires navigating technical interfaces, understanding data formats and mastering the intricacies of geospatial analysis — specialized skills that very few non-technical users possess. AI could streamline this process, reducing time to gain insights from Earth’s data to a matter of seconds.
This issue isn’t just a matter of convenience; it has real-world implications. For example, scientists who need to analyze historical data on hurricanes to improve predictive models, or policymakers who want to study deforestation patterns to implement environmental regulations, may find themselves unable to easily access the data they need. This inaccessibility affects a broad array of sectors, including agriculture, urban planning and disaster response, where timely insights from spaceborne data could make a significant difference.
Moreover, as new satellites with new instruments continue to launch and collect more data, NASA is constantly faced with the challenge of building new tools to manage and make sense of this growing repository. The agency explored emerging technologies that could not only streamline data discovery but also broaden accessibility, enabling more people to engage with the data and uncover new insights.
The solution: AI-powered data access through Microsoft Azure
To address these challenges, NASA IMPACT worked with Microsoft to develop an AI-driven customer copilot, called Earth Copilot, which could simplify data access and encourage a wider range of users to interact with its Earth Science data. Together, they built the proof of concept AI model that leverages Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform and advanced AI capabilities to transform how users can search, discover and analyze NASA’s geospatial data.
The key to NASA’s Earth Copilot lies in the integration of cloud-based technologies like Azure OpenAI Service, which provides access to powerful AI models and natural language processing capabilities that enable developers to integrate intelligent, conversational AI into their applications. This approach allows NASA to integrate AI into its existing data analysis platform — VEDA. These technologies together make it easier for users to search, discover and analyze Earth Science data
By combining these technologies, Earth Copilot enables users to interact with NASA’s data repository through plain language queries. Instead, they can simply ask questions such as “What was the impact of Hurricane Ian in Sanibel Island?” or “How did the COVID-19 pandemic affect air quality in the US?” AI will then retrieve relevant datasets, making the process seamless and intuitive.
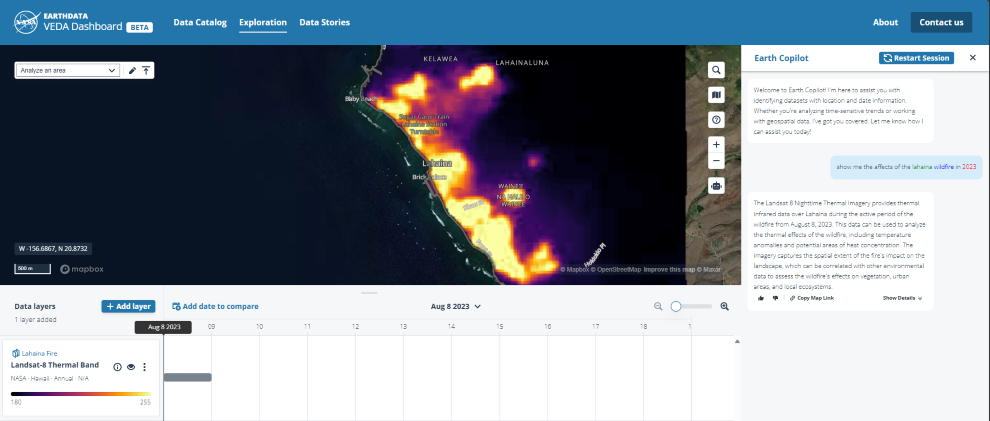
“Azure’s robust suite of services, including machine learning, data analytics and scalable cloud infrastructure, powers this AI prototype,” said Juan Carlos López, former NASA engineer and current Azure Specialist at Microsoft. “We’ve designed the system to handle complex queries and large datasets efficiently, ensuring that users can quickly find the information they need without getting bogged down by technical complexities. Our goal was to create a seamless, scalable solution that could evolve as NASA’s data, tools and applications grow.”
Democratizing data for open science
The collaboration between NASA IMPACT and Microsoft has resulted in a solution that democratizes access to spaceborne data, enabling a broader range of users to engage with NASA’s science data. This has significant benefits for the scientific community, as researchers can now spend less time on data retrieval and more on analysis and discovery. For example, climate scientists can quickly access historical data to study trends, while agricultural experts can gain insights into soil moisture levels to improve crop management.
Educators and teachers can use real-world examples to engage students in Earth Science, fostering curiosity and encouraging the next generation of scientists and engineers. Policymakers can leverage the data to make informed decisions on critical issues like climate change, urban development and disaster preparedness, ensuring they have the most accurate information at their fingertips.
“The vision behind this collaboration was to leverage AI and cloud technologies to bring Earth’s insights to communities that have been underserved, where access to data can lead to tangible improvements,” said Minh Nguyen, Cloud Solution Architect at Microsoft. “By enabling users to interact with the data through simple, plain language queries, we’re helping to democratize access to spaceborne information.”
The development of this AI prototype aligns with NASA’s Open Science initiative, which aims to make scientific research more transparent, inclusive and collaborative. By removing barriers to data discovery, NASA and Microsoft are setting the stage for a new era of discovery, where insights are not confined to a select few but can be explored and expanded by anyone curious about the world.
Looking ahead: Bridging the gap between data and insights
At the moment, the NASA Earth Copilot is available to NASA scientists and researchers to explore and test its capabilities. Any responsible deployment of AI technologies requires rigorous assessments to ensure the data and outputs cannot be misused. After a period of internal evaluations and testing, the NASA IMPACT team will explore the integration of this capability into the VEDA platform.
This collaboration exemplifies how technology can empower people, drive innovation and create positive change. Solutions like this will be essential in ensuring the benefits of data are shared widely, enabling more people to engage with, analyze and act upon information that shapes our world.