

Google has left Android users puzzled after the most recent update to the Google mobile app causes links shared from the app to now be prepended with a mysterious “search.app” domain.
As the Google app is a popular portal for searching the web for Android users and delivers a personalized content news feed referred to as Google Discover, it has sparked concern among those who noticed the new links.
What are these mysterious search.app links?
On November 6, 2024, Google rolled out its an Android version 15.44.27.28.arm64 of its app.
Ever since then, links viewed in Google’s in-app Chromium browser, when shared externally, are being prepended with a “search.app” domain.
BleepingComputer noticed the behaviour shortly after updating our Google app and we admit, the sight of a mysterious domain left us alarmed at first. Was our device compromised by adware?
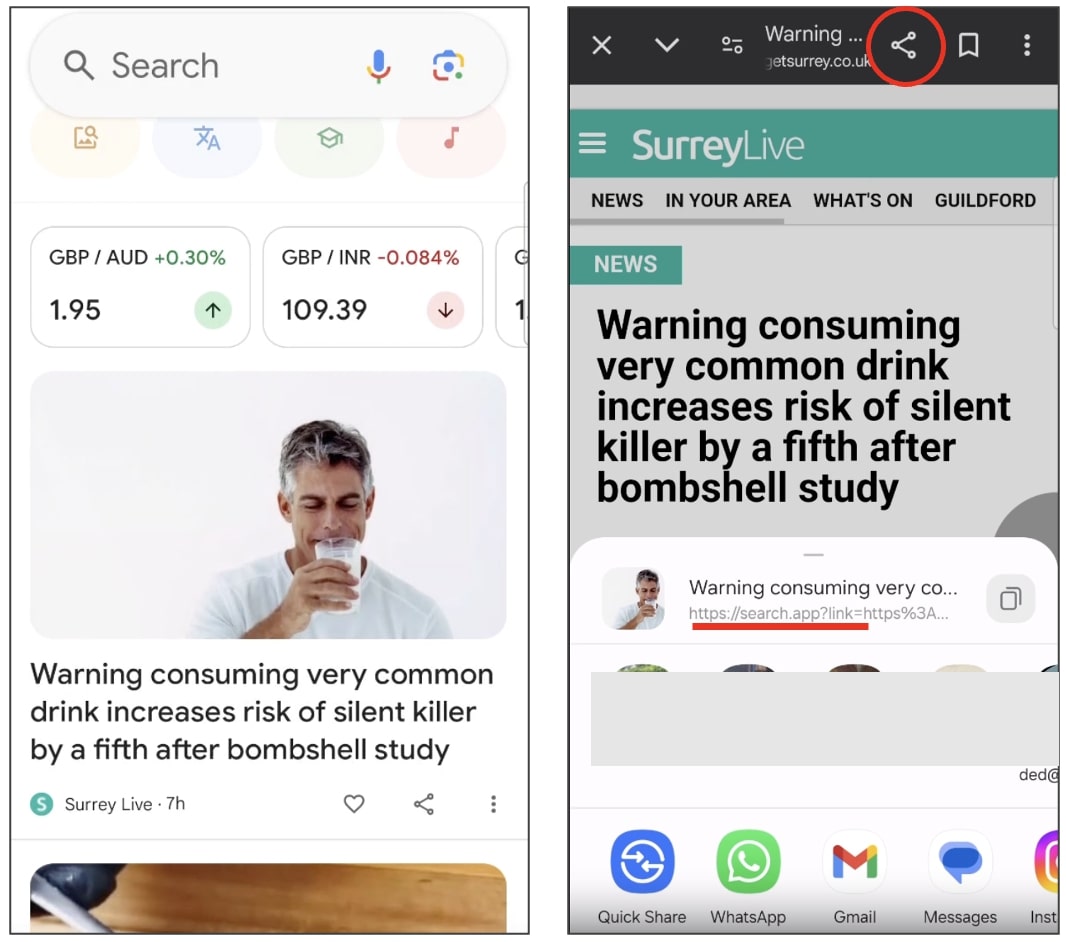
(BleepingComputer)
Our concerns are echoed by other users on Reddit this week.
“Recently (few days ago), I noticed that each link shared from the Google in-app web browser uses the ‘search.app’ domain,” asked Reddit user danilopiazza.
“For example, trying to share the link to the Reddit front Page, I get: https://search.app?link=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.reddit.com%2F&utm_campaign=…&utm_source=…”
“Is this a new feature from the Google app?”
A reader responded, “It seems like it. I’m getting this too. At first I thought I was somehow infected with some kind of malware, or somehow some setting unbeknownst to me got changed.”
Similar posts have emerged from others.
BleepingComputer observed links being shared via social media posts on X and Facebook via Google’s Android app this week are bearing the “search.app” domain too:
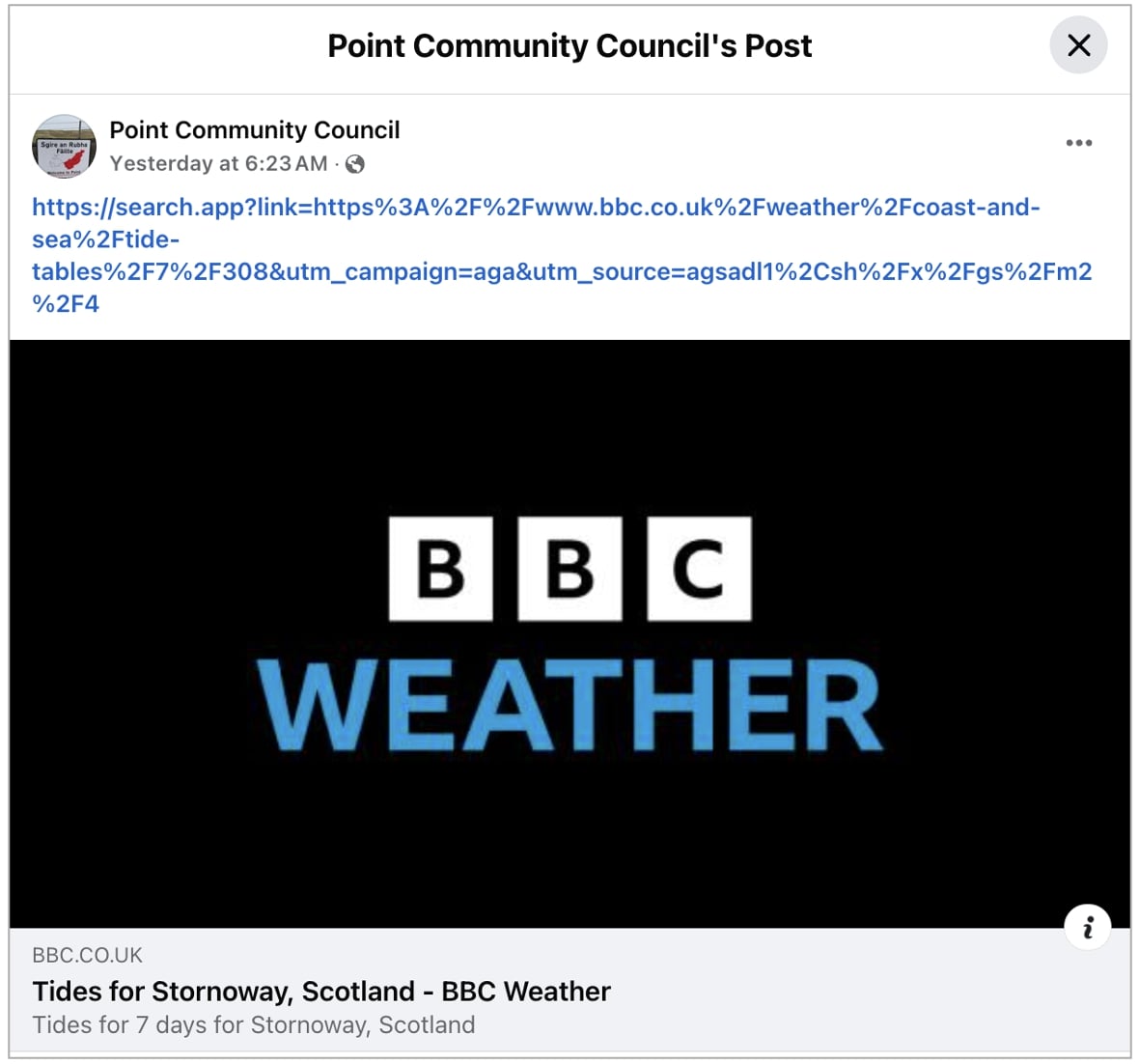
(BleepingComputer)
Is search.app safe?
Put simply, search.app is a URL redirector domain, much like t.co used by X (formerly Twitter), Google’s g.co, or Meta’s m.me.
Prepending links with “https://search.app?link=” gives Google enhanced visibility into how links are being externally shared by the Google app users and who are clicking on these links (i.e. referrers).
In addition to collecting analytics, by placing itself between users and external links by using the “search.app” domain, Google now has the ability to block traffic to phishing or hacked domains, should a website go rogue, or in the event that users are mass-sharing questionable content with each other (such as a scam site).
In our tests, navigating to search.app directly took us to an “Invalid Dynamic Link” page with a Firebase logo.
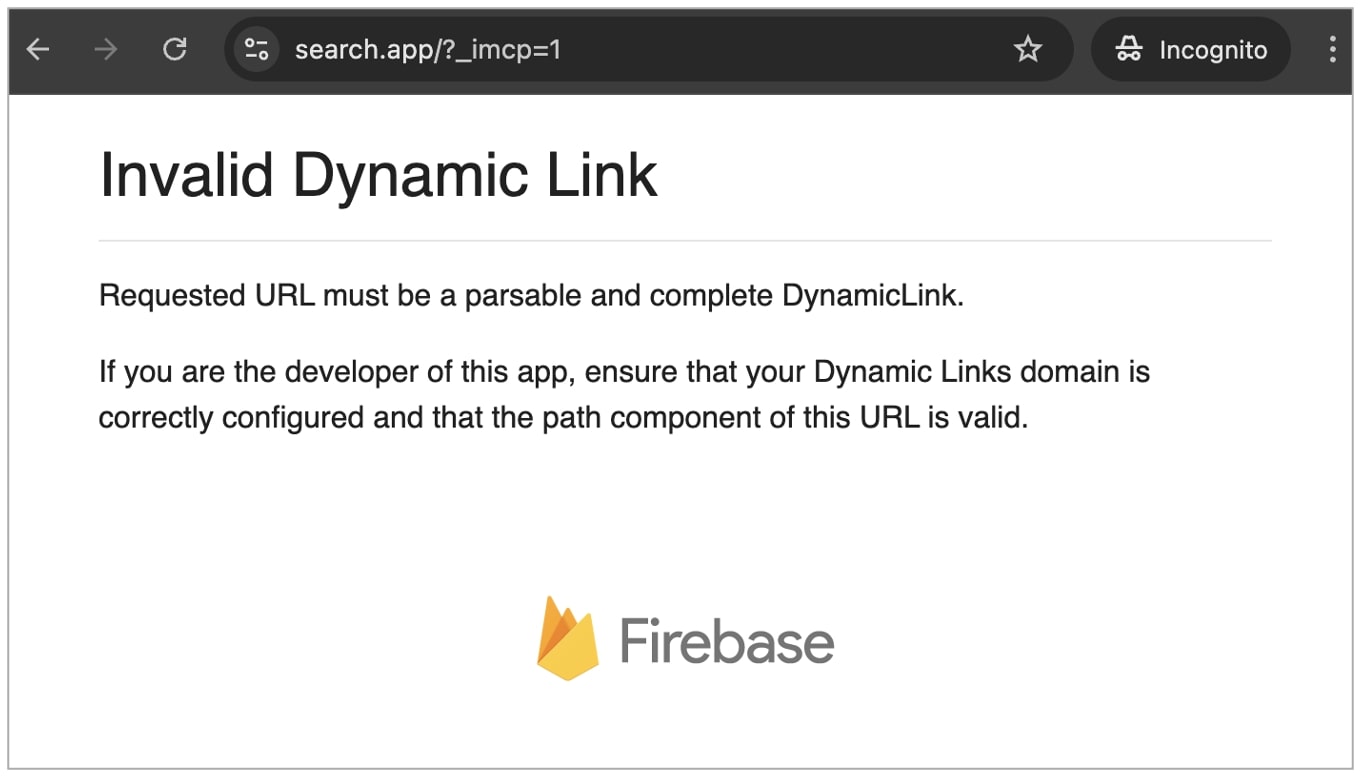
(BleepingComputer)
Firebase was acquired in 2014 by Google and has since become “Google’s mobile development platform that empowers you to quickly build and grow your app.”
We noticed a similar screen when navigating to Google’s another domain: https://search.app.goo.gl/
Ironically, Firebase Dynamic Links are deprecated and set to be shut down by August 2025.
WHOIS records for both search.app and goo.gl show Google LLC as the registrant organization and MarkMonitor as the registrar.
Shared TLS/SSL certificate and hosting
After publishing this piece, multiple BleepingComputer readers have pointed out an anomaly with SSL certificate issued to the ‘search.app’ domain.
To add confusion, the SSL certificate issued to ‘search.app’ shows the Common Name (CN) as fallacni.com.
BleepingComputer further noticed that the same SSL certificate is in use by more than a hundred domains, shown below, which are hosted on the same Firebase server (IP address 199.36.158.100).
It is possible that this due to the use of SSL/TLS technologies like Server Name Indication (SNI) which make it possible for multiple domains to be served over HTTPS on a shared hosting server, but is certainly anomalous. For comparison, certificate of Google’s search.app.goo.gl domain shows a CN set to ‘misc-sni.google.com’ and 216.58.212.206 as its server’s IP address.
fallacni.com
vireum.com
meatton.go1pos.com
digitley.co.in
www.mcseat.es
portfos.in
app.eluminate.in
dailypostbeat.com
www.hertzog-psychologue.fr
www.kanau.page
venits.com
www.weiwhite.com
jzz.me
golden-notes.io
peacedollar.org
ing-v3.sudahdistaging.in
merchantinstall.iomd.info
search.app
www.directions.healthcare
jellyjam.io
www.oeson.in
www.cutrite.app
api.onflix.app
cmouse.app
www.preaching.app
doc-internal.dalek.rs
honeycome.jp
podium.tools
www.dreamlin.com
fireacademy.io
mumbai.toobzgaming.com
risingstar.blackmint.io
qanda.link
editor.agua.app
aariz.me
link.nibo.com.br
site-result-auctions.farmgateauctions.com.au
beta.inhouseorders.io
typov.app
www.azvn.app
m.fiskal.app
genesix.ai
join.getostrich.app
swan-business-bugfix.ingogodev.net
compizza.lupi.delivery
bm.fusheng.info
preparhub.ca
go.holler.io
meeting.skylar.ai
easterbay.org
invest.scoutout.io
www.un-sichtbarespuren.de
cronometro.net
overthemoon.art
www.scenid.com
craftbyte.net
coloryourvoice.com
avantagecpo.com
fouronetwo.equiem.mobi
yo-dev.eparatodos.org
federalcafe.5loyalty.com
bstsst.com
b.ejsa.io
souscription.flitter.fr
flyvendas.com.br
flairtime.com
cinemetric.app
flyclub.app
www.endevagames.com
getpayify.app
justpic.app
selfy.ai
omnamo.app
davidvu.co.uk
console.shopezy.app
home.jooni.app
gpso.se
guicerpro.com
demo.pricely.app
speccon.cnfg.app
collctiv.app
productbacklog.dev
app1.posible.in
bookmark.undef.in
jeyhid.com
retro-it.com
rakesfieldandpeach.com
digitalnepalsolution.com
ryandine.com
dranandcardiocare.com
desiderioalmansa.com
vekend.com
strozu.com
hausasteri.com
bishoyriad.com
harshalplus.com
deliveryhub.app
eplise.com
ultrasiteservices.co.uk
reciproitsolutions.com
While thus far, the search.app redirector URLs appears to be safe and officially operated by Google, the sheer lack of documentation surrounding the domain is odd, as is the lack of its mention in public changelogs of Google’s open source projects, such as Android or Chromium.
The rollout of the search app update is bound to alarm even more users in the coming days who may wonder if their device is behaving erratically or has been compromised by malware.
Is this is Google’s attempt at imitating Apple News which prepends links to external stories with https://apple.news?
In the past, Google Chrome’s use of strange GVT1.com domains has drawn the scrutiny of even the most skilled researchers due to the lack of public documentation surrounding these domains.
BleepingComputer approached Google for comment in advance of publishing and we are awaiting a response.
Update, 8 November 2024 10:35 AM ET: Added section on ambigious SSL certificate presented by search.app.