
A recent report from Palo Alto Networks’s Unit 42 exposes the persistent and evolving threat of DNS hijacking, a stealthy tactic cybercriminals use to reroute internet traffic. By leveraging passive DNS analysis, the cybersecurity company also provided real-world examples of recent DNS hijacking attacks — highlighting the urgency of countering this hidden danger.
What is DNS hijacking?
DNS hijacking involves modifying the responses from targeted DNS servers, redirecting users to attacker-controlled servers instead of the legitimate ones they intend to reach.
DNS hijacking can be done in several ways:
- Gaining control of the domain owner’s account, providing access to DNS server settings: In this scenario, the attacker possesses valid user credentials with the authority to directly change the DNS server configuration. The attacker could also have valid credentials for the domain registrar or DNS service provider and change the configuration.
- DNS cache poisoning: The attacker impersonates a DNS nameserver and forges a reply, leading to attacker-controlled content instead of the legitimate one.
- Man-in-the-Middle attack: The attacker intercepts the user’s DNS queries and provides results that redirect the victim to the attacker-controlled content. This only works if the attacker is in control of a system implicated in the DNS query/answer process.
- Modifying DNS-related system files, such as the host file in Microsoft Windows systems. If the attacker has access to that local file, it is possible to redirect the user to attacker-controlled content.
Attackers generally use DNS hijacking to redirect users to phishing websites that look similar to the intended websites or to infect the users with malware.
Detecting DNS hijacking with passive DNS
The Unit 42 report described a method to detect DNS hijacking via passive DNS analysis.
What is passive DNS?
Passive DNS describes terabytes of historical DNS queries. In addition to the domain name and the DNS record type, passive DNS records generally contain a “first seen” and a “last seen” timestamp. These records allow users to trace the IP addresses a domain has directed users to over time.
For an entry to appear in passive DNS, it must be queried by a system whose DNS queries are recorded by passive DNS systems. This is why the most comprehensive passive DNS information generally comes from providers with high query volumes, such as ISPs or companies with extensive customer bases. Subscribing to a passive DNS provider is often advisable, as they collect more DNS queries than the average company, offering a more complete view than local DNS queries alone.
SEE: Everything You Need to Know about the Malvertising Cybersecurity Threat (TechRepublic Premium)
Detecting DNS hijacking
Palo Alto Network’s method for detecting DNS hijacking begins by identifying never-seen-before DNS records, as attackers often create new records to redirect users. Never-seen-before domain names are excluded from detection because they lack sufficient historical information. Invalid records are also removed at this step.
The DNS records are then analyzed using passive DNS and geolocation data based on 74 features. According to the report, “some features compare the historical usage of the new IP address to the old IP address of the domain name in the new record.” The goal is to detect anomalies that could indicate a DNS hijack operation. A machine-learning model then provides a probability score based on the analysis.
WHOIS records are also checked to prevent a domain from being re-registered, which generally leads to a complete IP address change that could be detected as DNS hijack.
Finally, active navigations are conducted on the domains’ IP addresses and HTTPS certificates. Identical results indicate false positives and can therefore be excluded from DNS hijacking operations.
DNS hijack statistics
From March 27 to Sept. 21 2024, researchers processed 29 billion new records, 6,729 of which were flagged as DNS hijacking. This resulted in an average of 38 DNS hijack records per day.
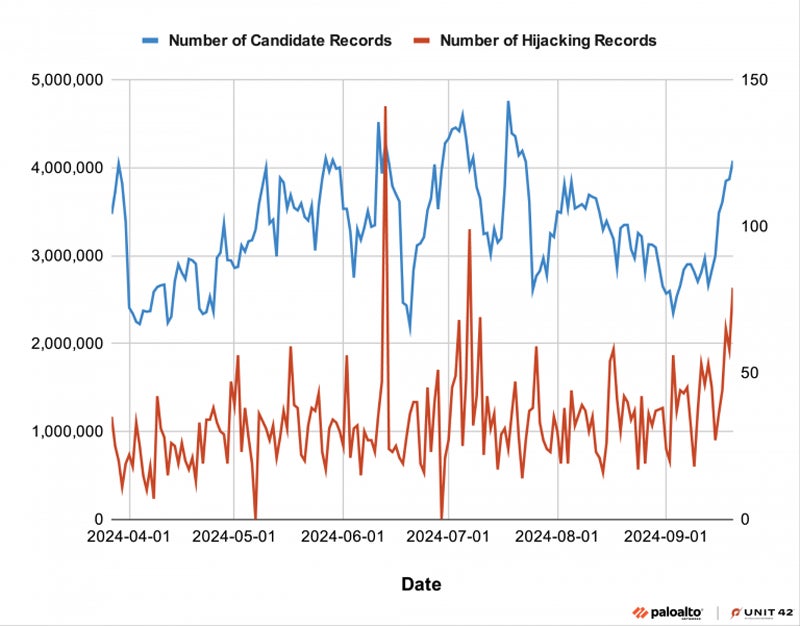
Unit 42 indicates that cybercriminals have hijacked domains to host phishing content, deface websites, or spread illicit content.
DNS hijacking: Real-world examples
Unit 42 has seen multiple DNS hijack cases in the wild, mostly for cybercrime purposes. Yet it is also possible to use DNS hijacking for cyberespionage.
Hungarian political party leads to phishing
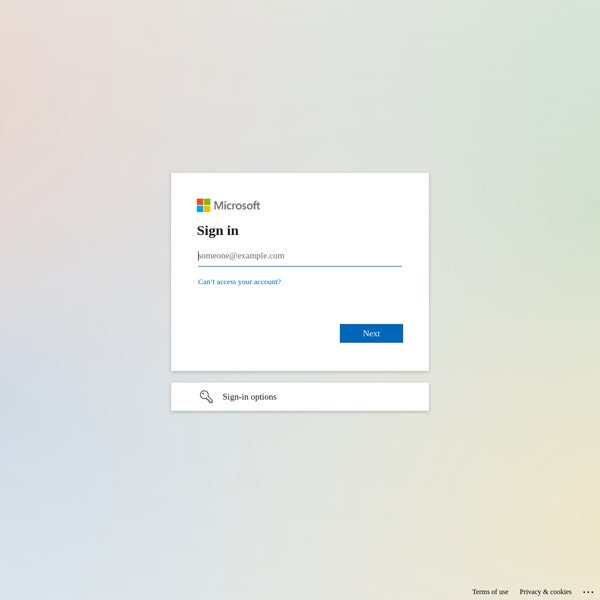
One of the largest political opposition groups to the Hungarian government, the Democratic Coalition (DK), has been hosted on the same subnet of IP addresses in Slovakia since 2017. In January 2024, researchers detected a change in the DK’s website, which suddenly resolved to a new German IP address, leading to a Microsoft login page instead of the political party’s usual news page.
US company defaced
In May 2024, two domains of a leading U.S. utility management company were hijacked. The FTP service, which has led to the same IP address since 2014, suddenly changed. The DNS nameserver was hijacked using the attacker-controlled ns1.csit-host.com.
According to the research, the attackers also used the same nameservers to hijack other websites in 2017 and 2023. The goal of the operation was to show a defaced page from an activist group.
How companies can protect themselves from this threat
To protect from these threats, the report suggested that organizations:
- Deploy multi-factor authentication to access their DNS registrar accounts. Establishing a whitelist of IP addresses allowed to access DNS settings is also a good idea.
- Leverage a DNS registrar that supports DNSSEC. This protocol adds a layer of security by digitally signing DNS communications, making it more difficult to intercept and spoof data for threat actors.
- Use networking tools that compare DNS queries results from third-party DNS servers — such as those from ISPs — to the DNS queries results obtained when using the company’s usual DNS server. A mismatch could indicate a change in DNS settings, which might be a DNS hijacking attack.
In addition, all hardware, such as routers, must have up-to-date firmware, and all software must be up-to-date and patched to avoid being compromised by common vulnerabilities.
Disclosure: I work for Trend Micro, but the views expressed in this article are mine.