.jpg)
.jpg)
Google Play, the official store for Android, distributed over a period of one year more than 200 malicious applications, which cumulatively counted nearly eight million downloads.
The data was collected between June 2023 and April 2024 by threat intelligence researchers at Zscaler, who identified and analyzed malware families both on Google Play and other distribution platforms.
The most common threats the researchers discovered on the official Android app store include:
- Joker (38.2%): Info-stealer and SMS message grabber that subscribes victims to premium services
- Adware (35.9%): Apps that consume internet bandwidth and battery to load either intrusive foreground ads or invisible ads in the background, generating fraudulent ad impressions
- Facestealer (14.7%): Facebook account credential stealers that overlay phishing forms on top of legitimate social media applications
- Coper (3.7%): Info-stealer and SMS message interceptor that can also perform keylogging and overlay phishing pages
- Loanly Installer (2.3%)
- Harly (1.4%): Trojan apps that subscribe victims to premium services
- Anatsa (0.9%): Anatsa (or Teabot) is a banking trojan that targets over 650 applications of banks worldwide
Earlier this year in May, the same researchers alerted of more than 90 malicious apps on Google Play, with a download count of 5.5 million.
Although Google has security mechanisms to detect malicious applications, threat actors still have some tricks to bypass the verification process. In a report last year, the Google Cloud security team described the ‘versioning‘, a method that delivers malware through application updates or by loading it from servers controlled by the attacker.
Regardless of the method used to deliver malware through Google Play, some campaigns are more successful than others. While Zscaler’s report focused on Android malware that is more common, other researchers discovered campaigns that also used Google Play to distribute malware to millions.
In one case, the Necro malware loader for Android was downloaded 11 million times through just two apps published on the official store.
In another case, the Goldoson Android malware was detected in 60 legitimate apps that cumulatively had 100 million downloads.
Last year, the SpyLoan was found in apps on Google Play that had been downloaded more than 12 million times.
Nearly half of the malicious apps that Zscaler ThreatLabz discovered were published on Google Play under tools, personalization, photography, productivity, and lifestyle categories.
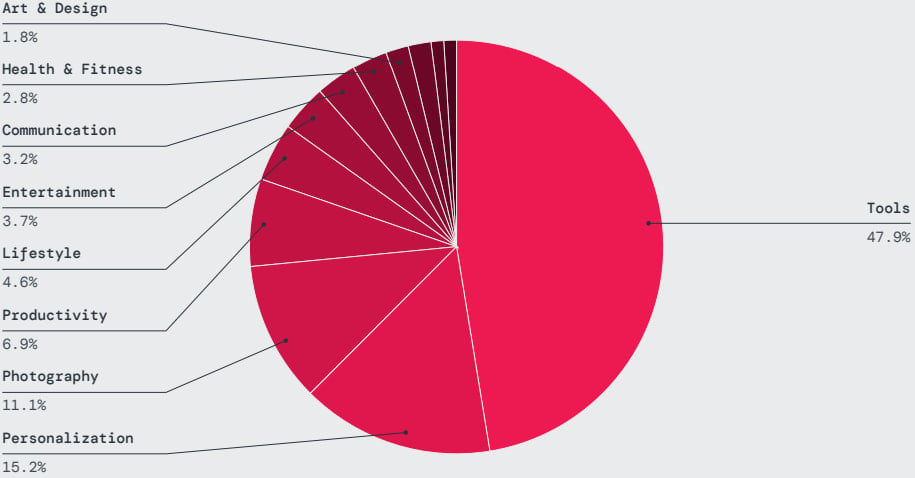
Source: Zscaler
In terms of malware blocks attempted this year, Zscaler reports that the trend shows an overall decline, as measured by blocked transactions.
On average, ThreatLabz recorded 1.7 million blocks per month, with 20 million blocks recorded throughout the analysis period, the most common threats being Vultur, Hydra, Ermac, Anatsa, Coper, and Nexus.
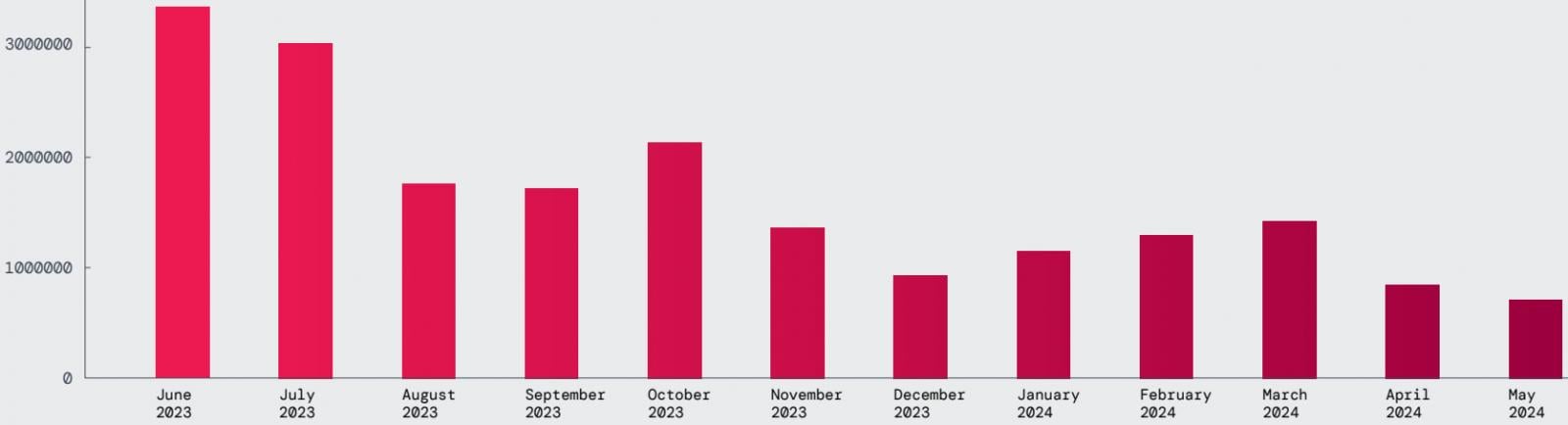
Source: Zscaler
Zscaler’s mobile threats report also shows a significant increase of spyware infections, driven primarily by SpyLoan, SpinOK, and SpyNote families. In the past year, the company registered 232,000 blocks of spyware activity.
The most targeted countries by mobile malware in the past year were India and the United States, followed by Canada, South Africa, and the Netherlands.
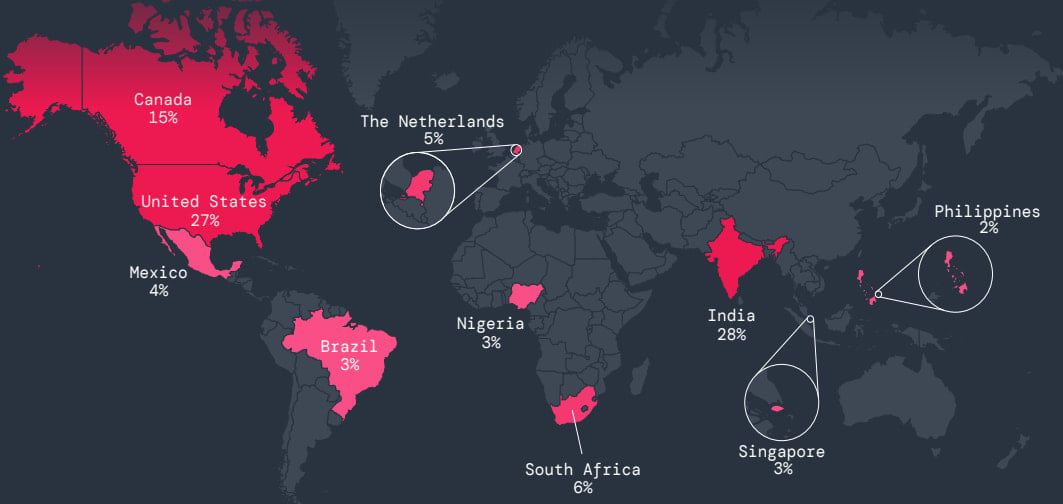
Source: Zscaler
According to the report, mobile malware targeted mostly the education sector, where the amount of blocked transactions increased by 136.8%. The services sector recorded a 40.9% increase, and chemicals and mining a 24% increase. All other sectors showed a general decline.
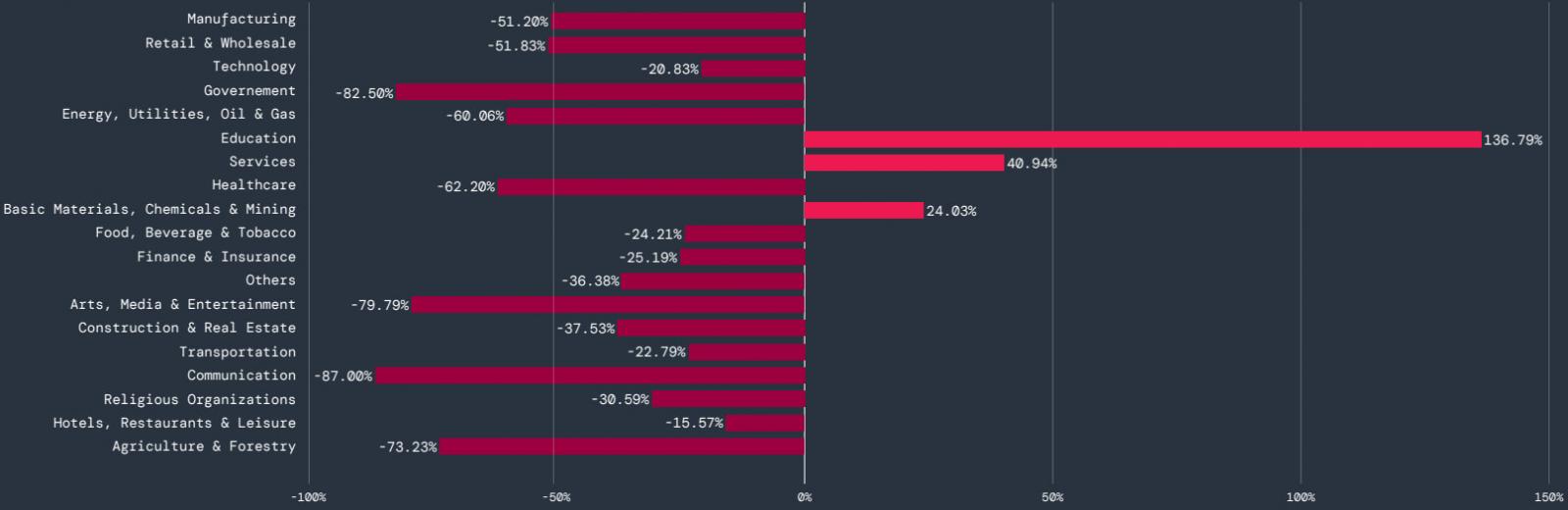
Source: Zscaler
To minimize the chances of getting infected by malware from Google Play, users are advised to read reviews from others to see what problems have been reported and check the application publisher.
Users should also check the permissions requested at installation time and abort the process if the app requires permissions that do not fit its activity.