The latest Sophos annual study of the real-world ransomware experiences of healthcare organizations explores the full victim journey, from attack rate and root cause to operational impact and business outcomes.
This year’s report sheds light on new areas of study for the sector, including an exploration of ransom demands vs. ransom payments and how often healthcare organizations receive support from law enforcement bodies to remediate the attack.
Download the report to get the full findings.
Attack rates have increased, and so have recovery costs
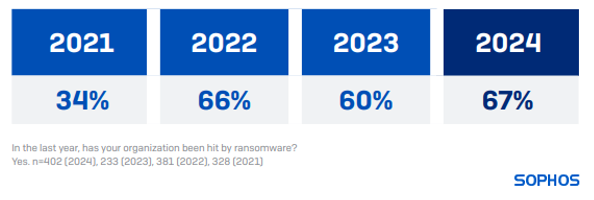
67% of healthcare organizations were hit by ransomware in 2024, up from 60% reported in our 2023 study. Healthcare’s ransomware attack rate this year is almost double that reported by the sector in 2021 (34%).
95% of healthcare organizations hit by ransomware in the past year said that cybercriminals attempted to compromise their backups during the attack. Of the attempts, two-thirds (66%) were successful. This is one of the highest rates of backup compromises, with only the energy, oil/gas and utilities (79%) and education (71%) sectors reporting higher rates.
74% of ransomware attacks on healthcare organizations resulted in data encryption, almost identical to the encryption rate reported in 2023 (73%). The sector reported a drop in extortion-only attacks, with only a single respondent reporting such an attack, compared to 4% in our 2023 study.
The mean cost in healthcare organizations to recover from a ransomware attack was $2.57M in 2024, an increase from the $2.20M reported in 2023.
Devices impacted in a ransomware attack
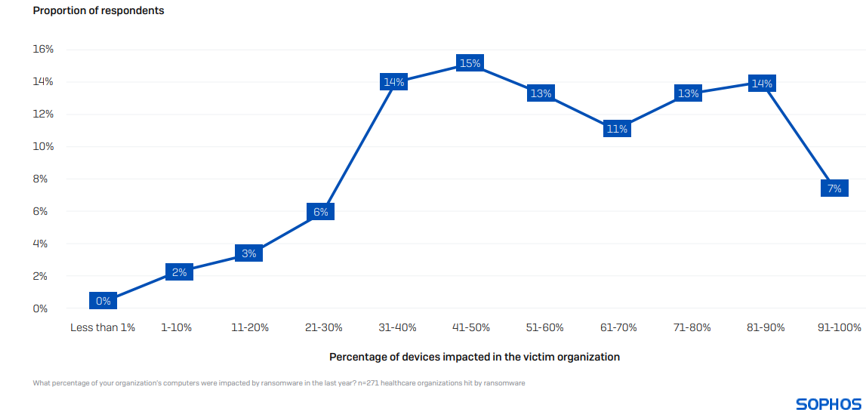
On average, 58% of computers in healthcare organizations are impacted by a ransomware attack, higher than the cross-sector average of 49%. Having your full environment encrypted is extremely rare, with only 7% of organizations reporting that 91% or more of their devices were impacted.
Propensity to pay the ransom has increased
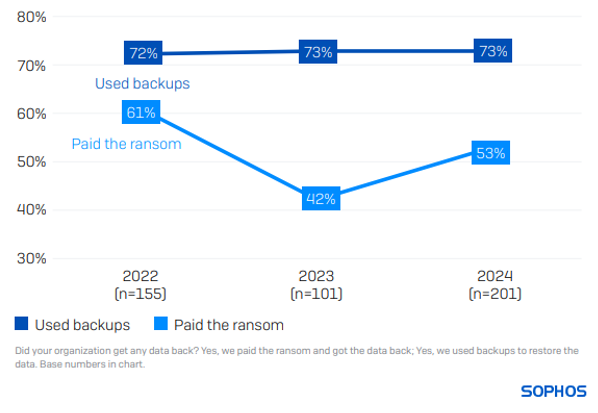
73% of healthcare organizations restored encrypted data using backups, and 53% paid the ransom to get data back. In comparison, globally, 68% used backups and 56% paid the ransom.
Over the last three years, the healthcare sector’s use of backups has remained steady (73% in 2023; 72% in 2022). However, the propensity of healthcare organizations to pay ransom has increased considerably in the last year (42% in 2023), although it remains lower than the 61% reported in 2022.
A notable change over the last year is the increase in the propensity for victims to use multiple approaches to recover encrypted data (e.g., paying the ransom and using backups). In this year’s study, 52% of healthcare organizations that had data encrypted reported using more than one method, three times the rate reported in 2023 (17%).
Healthcare victims rarely pay the initial ransom sum demanded
99 healthcare respondents whose organizations paid the ransom shared the actual sum paid, revealing that the average (median) payment was $1.5M in 2024.
Only 15% paid the initial ransom demand. 28% paid less than the original demand, while 57% paid more. On average, across all healthcare respondents, organizations paid 111% of the initial ransom demanded by adversaries.
Download the full report for more insights into ransom payments and many other areas.
About the survey
The report is based on the findings of an independent, vendor-agnostic survey commissioned by Sophos of 5,000 IT/cybersecurity leaders across 14 countries in the Americas, EMEA, and Asia Pacific, including 402 from the healthcare sector. All respondents represent organizations with between 100 and 5,000 employees. The survey was conducted by research specialist Vanson Bourne between January and February 2024, and participants were asked to respond based on their experiences over the previous year.